
Safer Using – Cathinones
About Cathinones Cathinone is a stimulant drug found in the leaves of khat (Catha edulis) which are chewed in Africa…
Tiletamine is a dissociative anaesthetic used in veterinary medicine to immobilise, sedate or anaesthetise animals for surgery, most commonly alongside zolazepam in a combination called Telazol or Zoletil.1 In Australia, tiletamine is classified as a Schedule 4 prescription only medication.2 The effects and safety of tiletamine in animals has been studied extensively, but its unique effects and dangers in humans—both long- and short-term—have not been documented. Tiletamine is sometimes incorrectly sold on the street as ketamine (colloquially known as polar bear ket) and recreational use among a small number of veterinarians has been documented.3,4,5,6 As a dissociative anaesthetic, tiletamine shares its mechanism of action with ketamine, but tiletamine is notably more potent and its effects last significantly longer.1
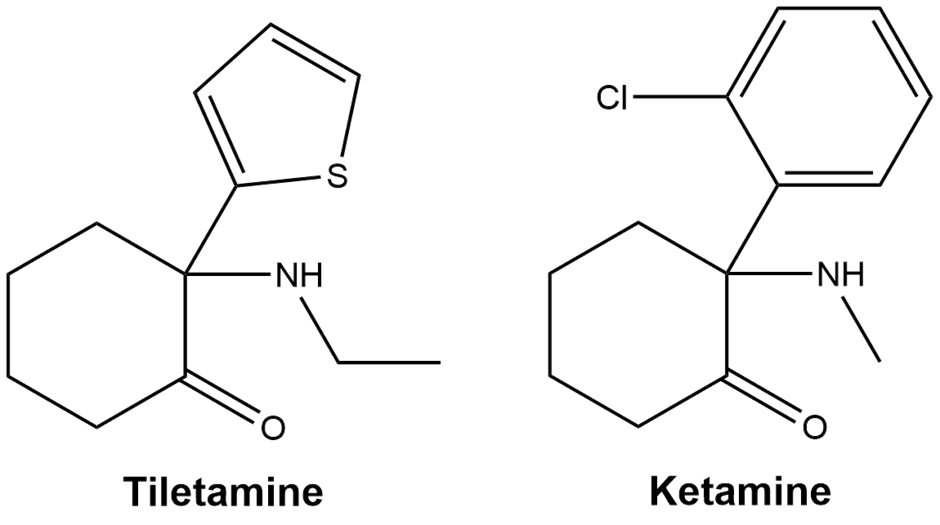
At CanTEST, Canberra’s fixed-site health and drug checking service, tiletamine has been detected numerous times in samples expected to be ketamine.4,5,6 As of April 2023, 81 samples of suspected ketamine were tested at CanTEST, and 26% of these samples contained another non-psychoactive substance and/or psychoactive drug, including tiletamine and 2F-NENDCK (a.k.a. “CanKet”).7 If you suspect your ketamine may be adulterated or contain a different drug entirely, consider taking a small sample to a drug checking service such as CanTEST. Ketamine testing kits (such as https://dancesafe.org/product/ketamine-testing-kit/) may also be able to differentiate between ketamine and tiletamine.
Since it is a dissociative anaesthetic, high doses of tiletamine have the potential to cause the loss of a person’s ability to move and loss of consciousness. For this reason, it is important for a person taking tiletamine to let someone else know they’ve taken it or preferably to have a trusted, sober person nearby to assist them if needed.
Due to its similar mechanism of action, tiletamine likely has subjective effects akin to ketamine, but its unique effects, if any, have not been widely documented. Notably, tiletamine lasts significantly longer than ketamine.1 One reddit user reported that they experienced persistent effects well after the peak of the experience, with the experience lasting approximately 4-6 hours in total.8 Other sources suggest tiletamine can last 2-5 hours in total when snorted.9 Another user reported a noticeable “hangover” feeling the day after using tiletamine.8
Tiletamine is more potent than ketamine, meaning it requires a smaller dose to achieve a similar intensity of effects.1 An exact dosage guide for tiletamine is not available but it is always recommended to start at a low dose and wait before redosing recreational drugs (start low and go slow).
A rough dosage guide for ketamine is available here: https://www.cahma.org.au/article/safer-using-ketamine/. A person dosing tiletamine could start with a dose that is half (or even less) of the desired dose of ketamine, wait for the effects to come on (up to 45 minutes), and then if necessary, work their way up in dosage until they achieve their desired intensity of effects.9
The risks associated with tiletamine overdose are largely unknown. Additionally, tiletamine may have unpredictable effects when mixed with other drugs or prescription medications. Since it is an anaesthetic, tiletamine has the potential to cause loss of coordination, motor control, or consciousness at high doses. Mixing tiletamine with depressants, including alcohol, GHB, and opioids, may be particularly dangerous since the combination could increase the risk of vomiting and unconsciousness. If a person falls unconscious on tiletamine, place them in the recovery position to prevent vomit aspiration. If you are concerned, consider seeking medical attention.
Some users of dissociatives seek a high-dose experience known as a “hole” or “holing”, which consists of complete dissociation and partial anaesthesia but allows the user to retain some degree of consciousness and memory of the experience.10 It is unknown whether tiletamine can produce a similar “hole” experience and what the correct dose required to achieve this would be. Taking very high doses of tiletamine may have unpredictable and potentially dangerous effects.
The long-term effects and toxicity of tiletamine have not been studied in humans and very few cases of severe reactions to tiletamine have been reported. One person was reportedly hospitalised due to involuntary movements in all of his limbs after taking Zoletil (tiletamine-zolazepam combination medication) for a period of two weeks.2 His movement disorder improved two weeks after stopping Zoletil, but he still had tremors on follow up after four months.2 A user on reddit also reported involuntary shaking in their legs and arms, vertigo, and vomiting after taking small doses of tiletamine for one month.11 This reportedly resolved two weeks after stopping tiletamine use.11
Frequent and long-term use of ketamine has been observed to cause damage to the lining of the bladder as well as kidney damage.12 This has been called ketamine bladder syndrome or ketamine-induced cystitis and the symptoms tend to mimic a urinary tract infection, namely:12
It is unknown whether tiletamine has the potential to cause a similar condition in humans or to what extent it does so. When administered at high doses in rabbits, tiletamine has been observed to cause kidney damage.1 If you are experiencing these symptoms and are concerned, consider visiting a non-judgmental health professional such as the GP or nurse at the CAHMA clinic.
[1] http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-380920-9.00002-X
[2] https://www.legislation.gov.au/Details/F2023L01294
[3] http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2008.12.030
[4] https://twitter.com/CanTESTCBR/status/1679638371302506496
[5] https://twitter.com/CanTESTCBR/status/1679638371302506496
[6] https://twitter.com/CanTESTCBR/status/1646685300549369857
[7] https://health.act.gov.au/sites/default/files/2023-07/CanTEST%20Final%20Evaluation%20Report_2023.pdf
[8] https://www.reddit.com/r/dissociatives/comments/qwmnrk/tiletamine_is_underrated/
[9] https://web.archive.org/web/20230606154717/https://drugs.tripsit.me/Tiletamine
[10] https://wiki.tripsit.me/wiki/Ketamine
[11] https://www.reddit.com/r/researchchemicals/comments/nezdxv/be_careful_with_tiletamine/
[12] https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.38247
Written by Darcy Lynch

About Cathinones Cathinone is a stimulant drug found in the leaves of khat (Catha edulis) which are chewed in Africa…

About Cannabis Cannabis (also known by its many slang names including marijuana, weed, Mary Jane, pot, dope, zaza, ganja, grass…

About Ketamine Ketamine (also known as ket, K, special K, or horse tranquiliser) is a dissociative anaesthetic belonging to a…